Вторичными структурами называются участки полипептидной цепи с упорядоченной конформацией, стабилизированной водородными связями (см. Вторичные структуры белков). В большинстве глобулярных белков присутствуют одновременно как α-спирали, так и β-складчатые листы. Кроме того, имеются участки с неупорядоченной структурой. Распространённым структурным элементом глобулярных белков является β-петля.
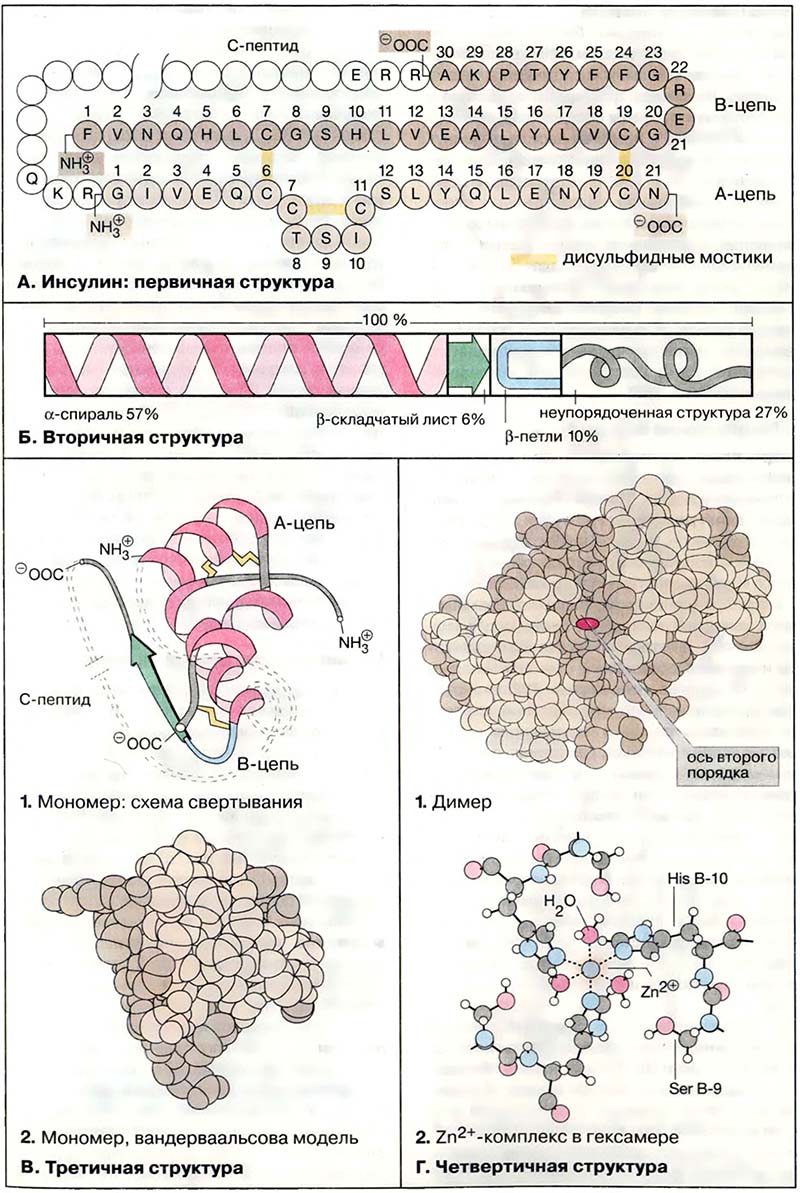
В молекуле инсулина участки, имеющие форму α-спирали, составляют 57 %, 6 % приходится на β-складчатую структуру, 10 % построено в виде β-петли, оставшиеся 27 % не имеют упорядоченной структуры.
В молекуле инсулина участки, имеющие форму α-спирали, составляют 57 %, 6 % приходится на β-складчатую структуру, 10 % построено в виде β-петли, оставшиеся 27 % не имеют упорядоченной структуры.
Статьи раздела «Глобулярные белки»:
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Паразитические нематоды растений и насекомых
Паразитические нематоды растений и насекомых В книге представлены обобщающие работы по современным теоретическим и ...
 Солитоны в молекулярных системах
Солитоны в молекулярных системах В монографии изложены новейшие подходы к изучению транспорта энергии и ...
 Влияние тяжелых металлов на процессы биохимического окисления органических веществ
Влияние тяжелых металлов на процессы биохимического окисления органических веществ В научной монографии рассмотрены основные направления очистки сточных вод, ...
 Stress — From Molecules to Behavior: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Neurobiology of Stress Responses
Stress — From Molecules to Behavior: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Neurobiology of Stress Responses This book comprehensively covers the molecular basis of stress responses of the nervous system, providing a unique and fundamental insight into the ...