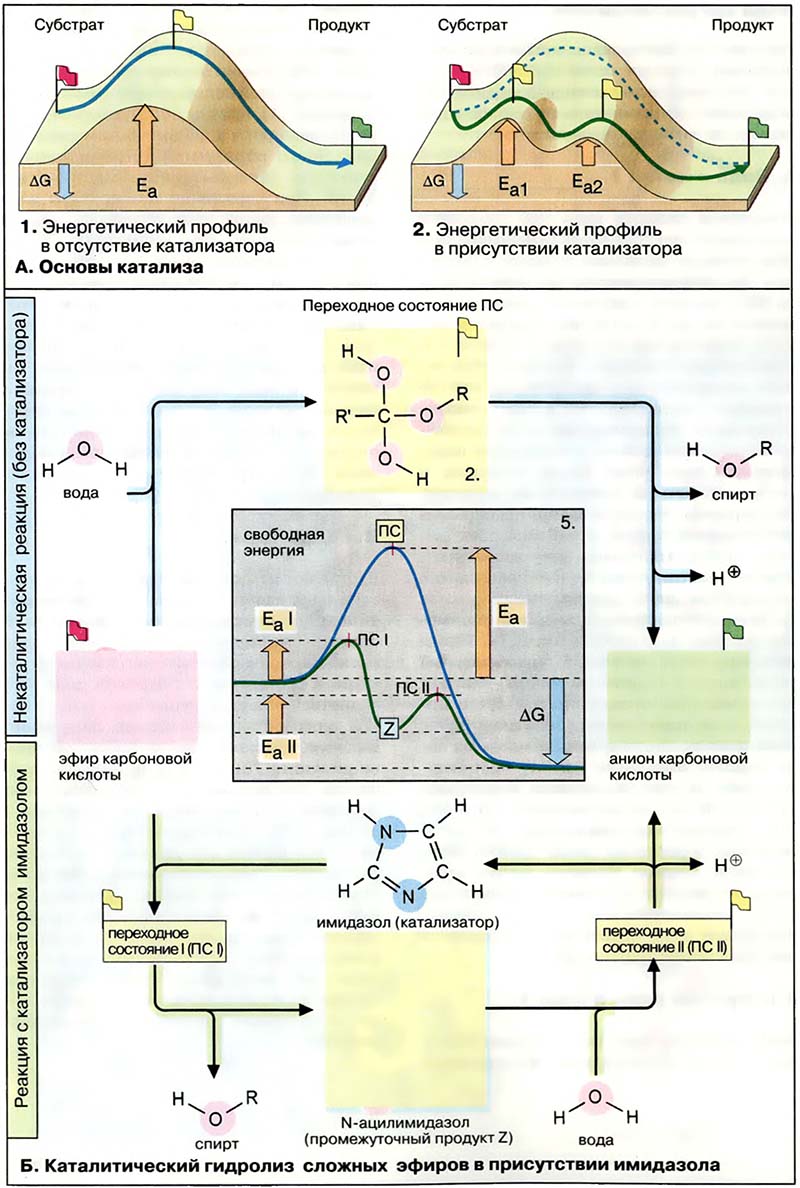
Катализаторы это вещества, которые влияют на скорость реакции, но сами при этом не расходуются. В живых клетках основными катализаторами являются ферменты (см. Деградация порфиринов). Очень немногие реакции катализируются молекулами РНК («рибозимы», см. Созревание РНК, Рибосомы: элонгация, терминация).
Статьи раздела «Катализ»:
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Fundamentals of Forensic DNA Typing
Fundamentals of Forensic DNA Typing An introductory text on forensic DNA analysis, written by the foremost expert in the field.
 Введение в молекулярную биологию
Введение в молекулярную биологию Книга представляет собой переработанный курс лекций, который авторы читают ...
В книге обобщаются современные достижения сравнительно новой отрасли знания, ...
 Нанотехнология белков. Протоколы, оборудование, области применения
Нанотехнология белков. Протоколы, оборудование, области применения В этой книге, написанной ведущими экспертами, собраны последние достижения в ...