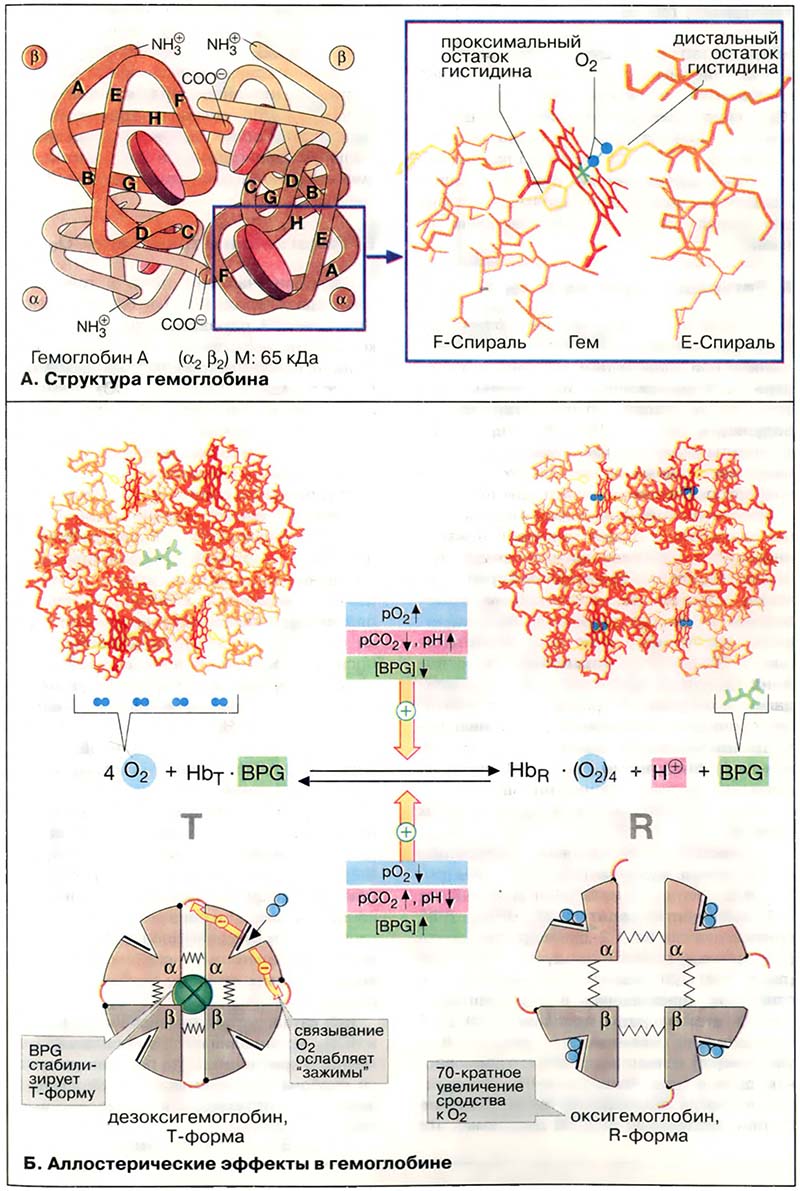
Главная функция эритроцитов (см. Кровь: состав и функции) — транспорт кислорода от лёгких в ткани и CO2 от тканей обратно в лёгкие. Высшие организмы нуждаются для этого в специальной транспортной системе, так как молекулярный кислород плохо растворим в воде: в 1 л плазмы крови растворимо только около 3,2 мл O2. Содержащийся в эритроцитах белок гемоглобин (Hb) способен связать в 70 раз больше — 220 мл O2/л. Содержание Hb в крови составляет 140-180 г/л у мужчин и 120-160 г/л у женщин, то есть вдвое выше по сравнению с белками плазмы (50-80 г/л). Поэтому Hb вносит наибольший вклад в образование рН-буферной ёмкости крови (см. Кислотно-основной баланс).
Статьи раздела «Гемоглобин»:
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 How to Build a Dinosaur: The New Science of Reverse Evolution
How to Build a Dinosaur: The New Science of Reverse Evolution A world-renowned paleontologist reveals groundbreaking science that trumps science fiction: how to grow a living dinosaur Over a decade after Jurassic ...
 Молекулярные механизмы взаимодействия эндотоксинов с клетками-мишенями
Молекулярные механизмы взаимодействия эндотоксинов с клетками-мишенями Открытие истинных рецепторов к эндотоксинам (липополисахаридам), сделанное на ...
 Влияние тяжелых металлов на процессы биохимического окисления органических веществ
Влияние тяжелых металлов на процессы биохимического окисления органических веществ В научной монографии рассмотрены основные направления очистки сточных вод, ...
 Biotechnology Annual R Volume 14 (Biotechnology Annual Review) (Biotechnology Annual Review)
Biotechnology Annual R Volume 14 (Biotechnology Annual Review) (Biotechnology Annual Review) Biotechnology is a diverse, complex, and rapidly evolving field. Students and experienced researchers alike face the challenges of staying on top of ...