| Биомолекулы. Углеводы | |
|---|---|
| Углеводы Углеводы (сахара) — группа природных полигидроксиальдегидов и полигидроксикетонов с общей формулой (CH2O)n. Группа включает простые сахара (моносахариды) и их высокомолекулярные аналоги, олигосахариды ... | |
| А. Биологические функции углеводов Полисахариды, прежде всего крахмал и некоторые дисахариды, являются важными (хотя и не жизненно необходимыми) компонентами питания (см. Питание. Органические вещества). В кишечнике они расщепляются до моносахаридов, которые затем всасываются ... | 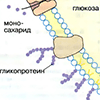 |
| Б. Структура моносахаридов Важнейший природный моносахарид, D-глюкоза, является алифатическим альдегидом, содержащим шесть углеродных атомов, пять из которых имеют гидроксильные группы (1). Поскольку атомы C-2 —C-5 являются хиральными центрами (см ... | 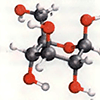 |
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
Учебное пособие, в котором авторы из США и Великобритании в доступной форме ...
 Practical Forensic Microscopy: A Laboratory Manual
Practical Forensic Microscopy: A Laboratory Manual Forensic Microscopy: A Laboratory Manual will provide the student with a practical overview and understanding of the various microscopes and ...
 Ферментативная кинетика. Справочник по механизмам реакций
Ферментативная кинетика. Справочник по механизмам реакций Много лет тому назад под руководством профессора Е. Е. Селькова автором была ...
 Role of TCF in body axis formation: Discovery of a Dual Action of XTCF-3 in Xenopus Body Axis Formation
Role of TCF in body axis formation: Discovery of a Dual Action of XTCF-3 in Xenopus Body Axis Formation A novel role of TCF family in body axis formation. Revolutionary high impact discoveries are described, elucidating the missing link in the Wnt ...