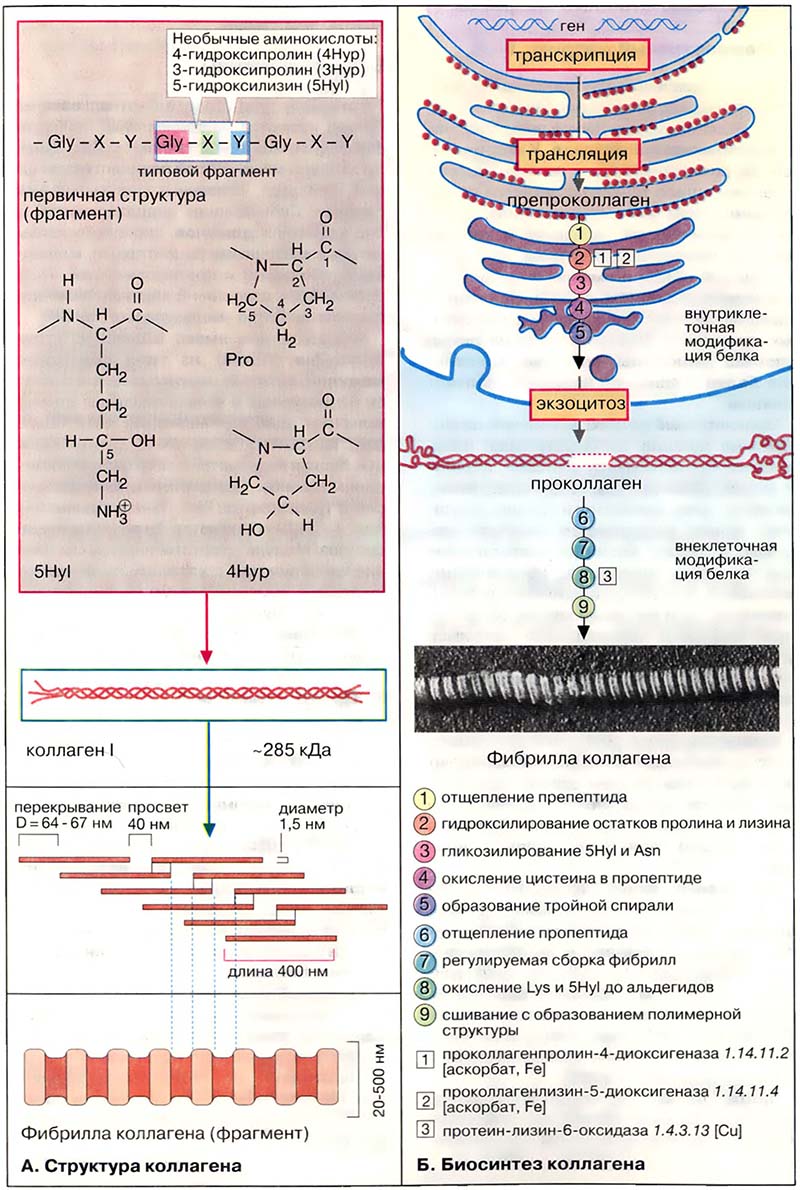
Типичная молекула коллагена состоит из трёх полипептидных цепей разных типов (α-спиралей), скрученных в виде правой тройной спирали. В свою очередь полипептидные цепи построены из часто повторяющихся фрагментов, имеющих характерную последовательность -Gly-X-Y- (см. Структурные белки). Каждым третьим аминокислотным остатком является глицин. Пролин (Pro) часто встречается в положениях X, положение Y может быть занято как пролином, так и 4-гидроксипролином (4Hyp). Кроме того, молекула коллагена содержит остатки 3-гидроксипролина (3Hyp) и 5-гидроксилизина (5Hyl). Присутствие в полипептидной цепи остатков гидроксиаминокислот является характерной особенностью коллагена. Остатки пролина и лизина гидроксилируются посттрансляционно, то есть после включения в полипептидную цепь. На одном из концов молекула коллагена сшита поперечными связями, образованными боковыми цепями остатков лизина. Количество поперечных связей возрастает по мере старения организма.
Известно по крайней мере 12 вариантов коллагена, характеризующихся различным сочетанием полипептидных α-цепей (α1-αЗ и др. подтипы). Наиболее общий тип коллагена I имеет следующую четвертичную структуру: [α1(I)]2α2(I). Это длинная нитевидная молекула с молекулярной массой 285 кДа.
Молекулы коллагенов обладают свойством спонтанно агрегировать с образованием более сложных структур, микрофибрилл и фибрилл. Большинство коллагенов образуют фибриллы цилиндрической формы (диаметром 20-500 нм) с характерными поперечными полосами, повторяющимися через каждые 64-67 нм.
Известно по крайней мере 12 вариантов коллагена, характеризующихся различным сочетанием полипептидных α-цепей (α1-αЗ и др. подтипы). Наиболее общий тип коллагена I имеет следующую четвертичную структуру: [α1(I)]2α2(I). Это длинная нитевидная молекула с молекулярной массой 285 кДа.
Молекулы коллагенов обладают свойством спонтанно агрегировать с образованием более сложных структур, микрофибрилл и фибрилл. Большинство коллагенов образуют фибриллы цилиндрической формы (диаметром 20-500 нм) с характерными поперечными полосами, повторяющимися через каждые 64-67 нм.
Статьи раздела «Коллагены»:
- Коллагены
- А. Структура коллагенов
- Б. Биосинтез коллагена
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Физика белка. Курс лекций с цветными и стереоскопическими иллюстрациями и задачами
Физика белка. Курс лекций с цветными и стереоскопическими иллюстрациями и задачами Физика белка простирается от классификации и принципов устройства белков ...
В книге обобщаются современные достижения сравнительно новой отрасли знания, ...
 How to Build a Dinosaur: The New Science of Reverse Evolution
How to Build a Dinosaur: The New Science of Reverse Evolution A world-renowned paleontologist reveals groundbreaking science that trumps science fiction: how to grow a living dinosaur Over a decade after Jurassic ...