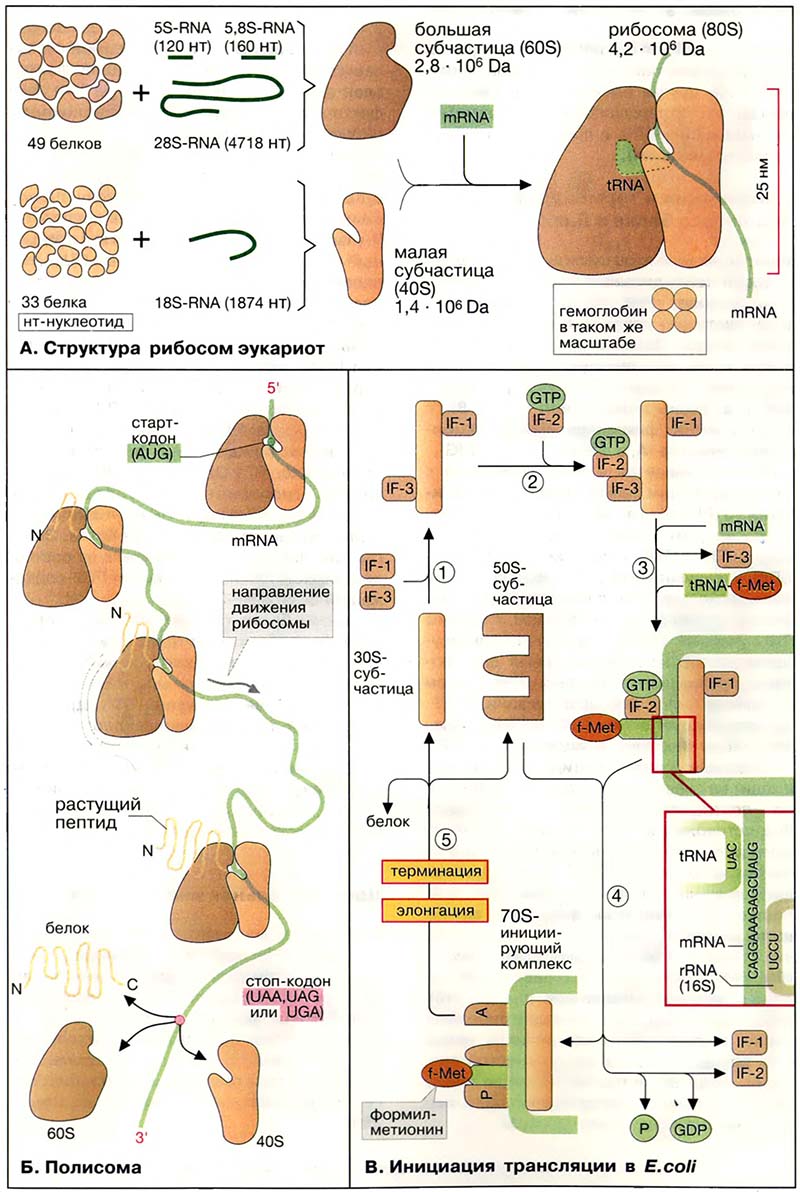
Рибосомы состоят из двух различных субчастиц, каждая из которых построена из рибосомной РНК [рРНК (rRNA)] и многих белков. Рибосомы и их субчастицы обычно классифицируют не по массам, а в соответствии с коэффициентами седиментации (см. Центрифугирование). Так, коэффициент седиментации полной эукариотической рибосомы составляет около 80 единиц Сведберга (80S), а коэффициент седиментации её субчастиц составляет 40S и 60S.
Меньшая 40S-субчастица состоит из одной молекулы 18S-pPHK и 30-40 белковых молекул. Большая 60S-субчастица содержит три типа рРНК с коэффициентами седиментации 5S, 5,8S и 28S и 40-50 белков (например, рибосомы гепатоцитов крысы включают 49 белков). В присутствии мРНК (mRNA) субчастицы объединяются с образованием полной рибосомы, масса которой примерно в 650 раз больше массы молекулы гемоглобина. Рибосомы имеют диаметр 20-200 нм и их можно видеть в электронный микроскоп. Структурная организация рибосом полностью не выяснена. Однако известно, что молекулы мРНК проходит через щель около характерной структуры в виде «рога» на малой субчастице, причём эта щель ориентирована как раз в промежуток между двумя субчастицами. тРНК также связываются вблизи этого участка. Для сравнения на схеме в том же масштабе показана молекула тРНК.
Рибосомы прокариот имеют аналогичную структуру, но они несколько мельче, чем эукариотические (коэффициенты седиментации полной рибосомы 70S, а субчастиц — 30S и 50S). Рибосомы митохондрий и хлоропластов близки к прокариотическим.
Меньшая 40S-субчастица состоит из одной молекулы 18S-pPHK и 30-40 белковых молекул. Большая 60S-субчастица содержит три типа рРНК с коэффициентами седиментации 5S, 5,8S и 28S и 40-50 белков (например, рибосомы гепатоцитов крысы включают 49 белков). В присутствии мРНК (mRNA) субчастицы объединяются с образованием полной рибосомы, масса которой примерно в 650 раз больше массы молекулы гемоглобина. Рибосомы имеют диаметр 20-200 нм и их можно видеть в электронный микроскоп. Структурная организация рибосом полностью не выяснена. Однако известно, что молекулы мРНК проходит через щель около характерной структуры в виде «рога» на малой субчастице, причём эта щель ориентирована как раз в промежуток между двумя субчастицами. тРНК также связываются вблизи этого участка. Для сравнения на схеме в том же масштабе показана молекула тРНК.
Рибосомы прокариот имеют аналогичную структуру, но они несколько мельче, чем эукариотические (коэффициенты седиментации полной рибосомы 70S, а субчастиц — 30S и 50S). Рибосомы митохондрий и хлоропластов близки к прокариотическим.
Статьи раздела «Рибосомы: инициация трансляции»:
- Рибосомы: инициация трансляции
- А. Структура рибосом эукариот
- Б. Полисома
- В. Инициация трансляции в E. coli
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Внутриклеточная Са2+-зависимая протеолитическая система животных
Внутриклеточная Са2+-зависимая протеолитическая система животных Монография представляет собой обобщающее издание, основанное на анализе ...
 Фотосинтез: физико-химический подход
Фотосинтез: физико-химический подход Подробно обосновывается предложенная автором (1995) принципиально новая концепция ...
 Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology
Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology Long considered the definitive work in its field, this new edition presents all the principles and practices readers need for a solid grounding in all ...
