| Биомолекулы. Пептиды и белки | |
|---|---|
| Молекулярные модели: инсулин На схеме А приведена молекулярная модель небольшого белка инсулина. Строение, биосинтез и функции этого важнейшего гормона подробно обсуждаются в других разделах (см. Метаболизм жиров, Кости, зубы и соединительные ткани). | |
| А. Инсулин (мономер) Мономер инсулина состоит из 51 аминокислотного остатка (см. Метаболизм жиров), т. е. по молекулярной массе (5,5 кДа) он вдвое уступает самому низкомолекулярному ферменту. Тем не менее инсулин остаётся типичным глобулярным белком. ... |  |
| Б. Инсулин (гексамер) До поступления в кровь инсулин накапливается B-клетками в островках Лангерганса в виде цинксодержащего гексамера (см. Кости, зубы и соединительные ткани). На схеме Б приведён гексамер (олигомер из 6 субъединиц) в упрощённом, ленточном, ... | 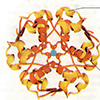 |
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
 История биологической химии. Истоки науки
История биологической химии. Истоки науки Книга посвящена первым шагам взаимодействия химии с биологией и медициной. В ней ...
 Защита от биоповреждений, вызываемых грибами
Защита от биоповреждений, вызываемых грибами Книга посвящена проблеме снижения химической и биологической опасности в сфере ...
Обобщены результаты, демонстрирующие многообразие конденсированных форм ...