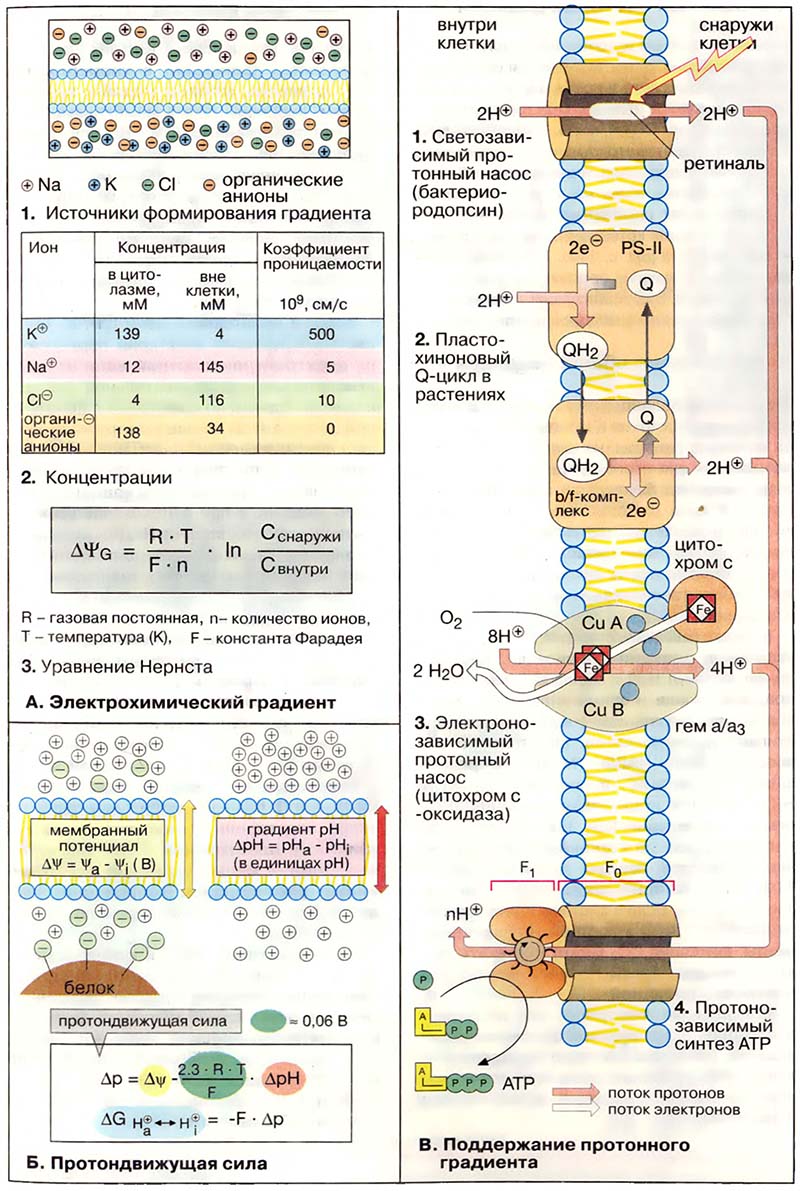
Наряду с макроэргическими соединениями другим местом накопления химической энергии являются биологические мембраны. В технике система, работающая за счёт разделения электрических зарядов непроводящим слоем, называется конденсатором. По принципу конденсатора функционируют биомембраны, разделяющие подобно изолирующему слою заряженные атомы и молекулы (ионы).
Статьи раздела «Сохранение энергии на мембранах»:
- Сохранение энергии на мембранах
- А. Электрохимический градиент
- Б. Протондвижущая сила
- В. Поддержание протонного градиента
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Интеллектуальные липидные наноконтейнеры в адресной доставке лекарственных веществ
Интеллектуальные липидные наноконтейнеры в адресной доставке лекарственных веществ Настоящая книга рассказывает о новейших достижениях в использовании липидов и ...
Учебное пособие освещает систематизированную совокупность современных знаний ...
 Атлас. Морфология крахмала и крахмалопродуктов
Атлас. Морфология крахмала и крахмалопродуктов В атласе приведены данные о морфологической характеристике нативных крахмалов: ...
