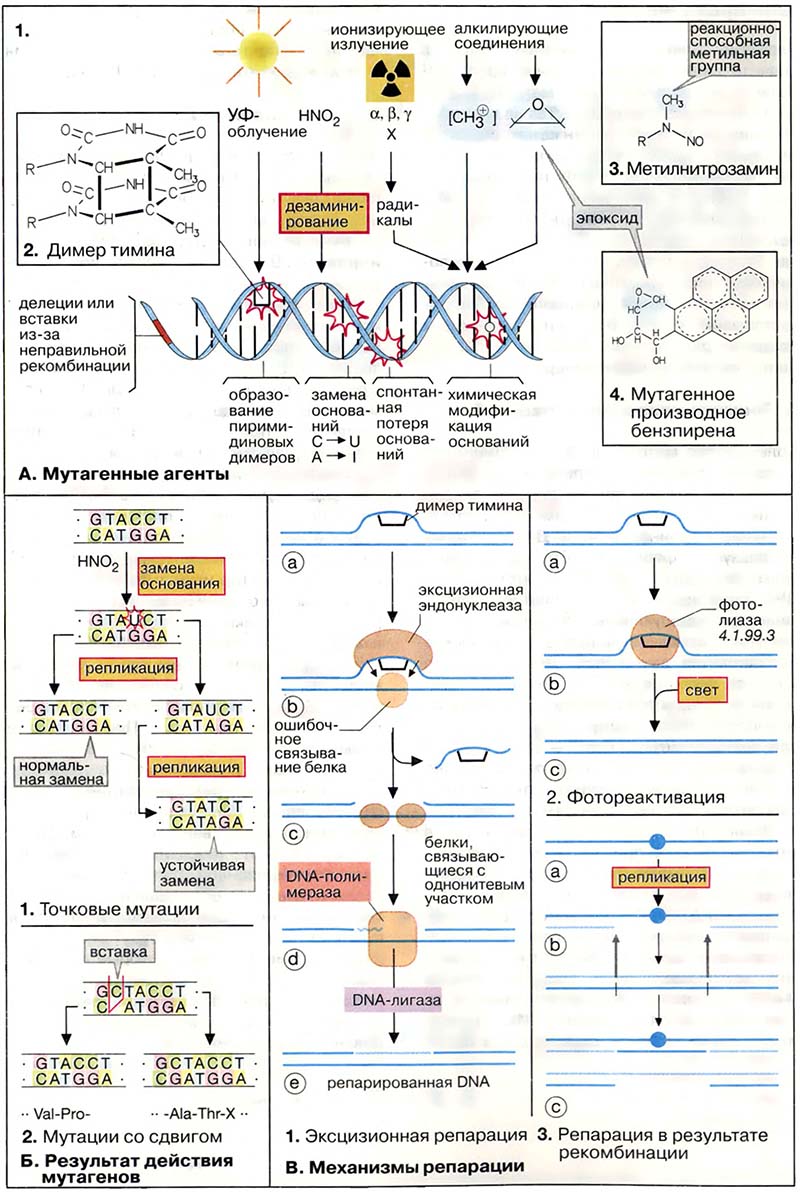
Генетическая информация кодируется последовательностью оснований ДНК и поэтому изменения в структуре или последовательности азотистых оснований приводят к мутациям. Многие мутагены вызывают нарушения регуляции роста и деления клеток и поэтому являются канцерогенными. Изменение в структуре генов (мутация) — важный фактор биологической эволюции. В то же время слишком высокая скорость мутаций ставит под вопрос существование индивидуальных организмов или целых видов. Поэтому клетки обладают механизмами восстановления (репарации), которые корректируют большинство изменений ДНК, вызываемых мутациями.
Статьи раздела «Мутация и репарация»:
- Мутация и репарация
- А. Мутагенные агенты
- Б. Результат действия мутагенов
- В. Механизмы репарации
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
В стенограмме публичной лекции характеризуется метод тканевых культур и ...
 Фотосинтез. В 2 томах (комплект)
Фотосинтез. В 2 томах (комплект) Книга, написанная в основном американскими авторами, представляет собой ...
 Биокатализ и биокатализаторы. Исторический очерк
Биокатализ и биокатализаторы. Исторический очерк Книга посвящена истории возникновения и развития двух основных проблем ...
