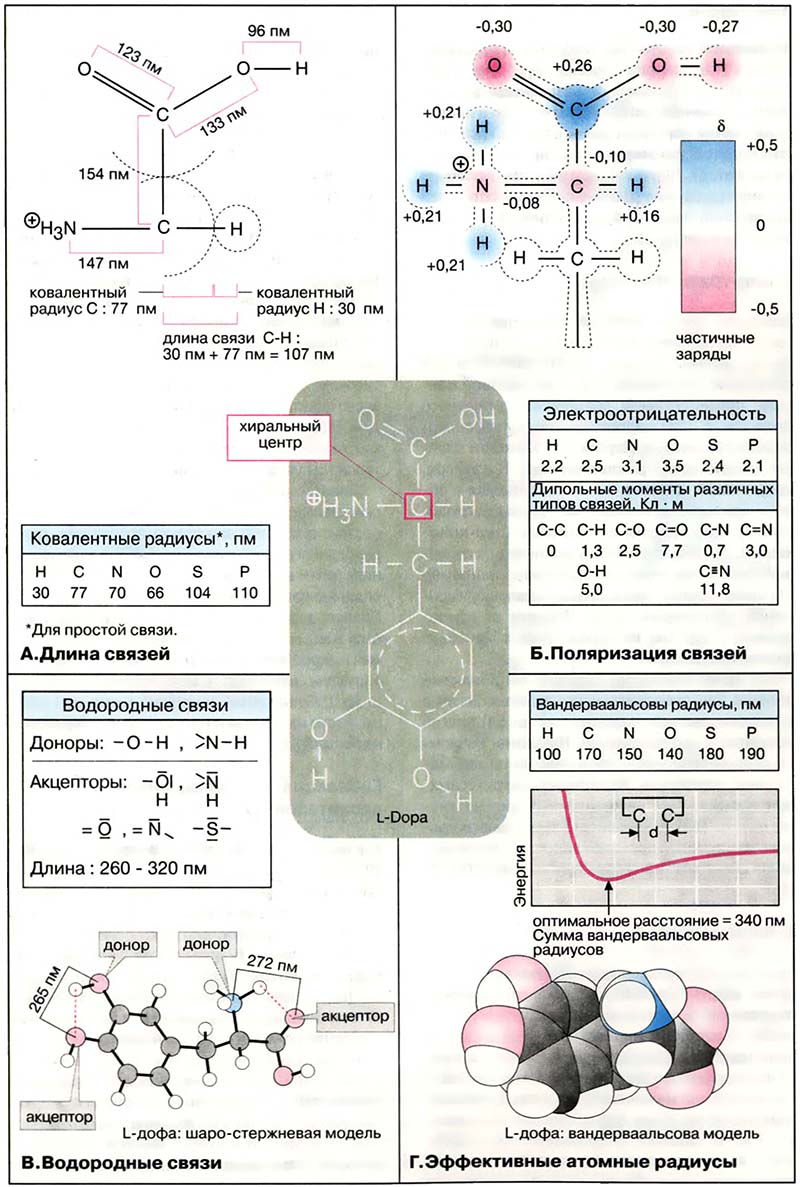
Физические и химические свойства молекул определяются их строением. Поэтому многие свойства могут быть предсказаны на основании структурной формулы. К таким свойствам относятся размеры, форма, до некоторой степени конформация молекул (то есть взаимное расположение отдельных атомов) при нахождении вещества в растворе и, наконец, реакционная способность. В этом разделе сведены параметры, на основании которых можно прогнозировать свойства соединений. Здесь также представлена пространственная структура одного из органических соединений — L-дигидроксифенилаланина [L-дофа (L-Dopa)], промежуточного продукта в биосинтезе катехоламинов (см. Медиаторы нервной системы).
Статьи раздела «Строение молекул»:
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Анализ биологических последовательностей
Анализ биологических последовательностей Предлагаемая книга отражает современное состояние сравнительно новой, но весьма ...
 Молекулярные механизмы взаимодействия эндотоксинов с клетками-мишенями
Молекулярные механизмы взаимодействия эндотоксинов с клетками-мишенями Открытие истинных рецепторов к эндотоксинам (липополисахаридам), сделанное на ...
 Fundamentals of Forensic DNA Typing
Fundamentals of Forensic DNA Typing An introductory text on forensic DNA analysis, written by the foremost expert in the field.
Учебник состоит из четырёх частей, включающих 15 глав, в которых изложены вопросы ...