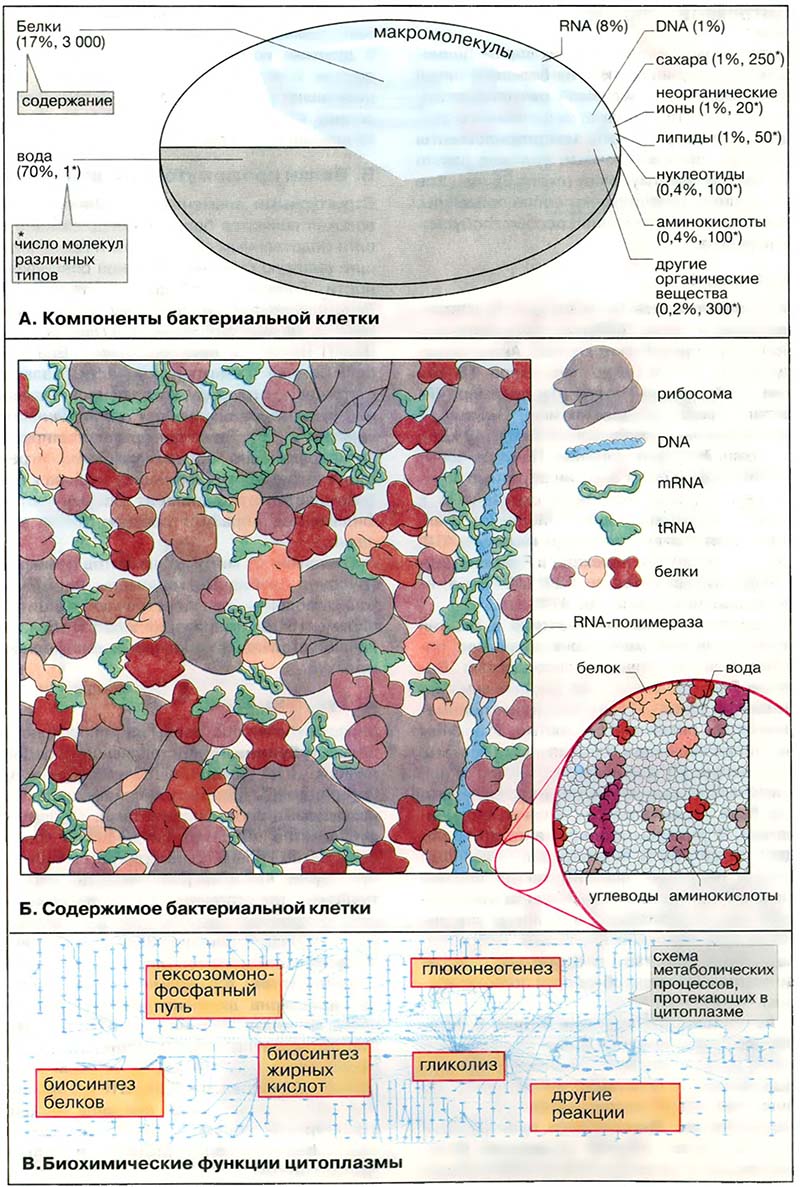
У эукариот цитоплазма составляет 50 % общего объёма клетки, то есть в количественном отношении является наиболее важной органеллой клетки. Цитоплазма — это главное реакционное пространство клетки. Здесь протекают большинство процессов деградации питательных веществ и синтеза структурных компонентов клетки, а также почти весь промежуточный метаболизм: гликолиз, гексозомонофосфатный путь, глюконеогенез, биосинтез жирных кислот, белков и т. п.
Статьи раздела «Клеточные компоненты и цитоплазма»:
- Клеточные компоненты и цитоплазма
- А. Компоненты бактериальной клетки
- Б. Содержимое бактериальной клетки
- В. Биохимические функции цитоплазмы
- Цитоскелет: состав
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Структура и стабильность биологических макромолекул
Структура и стабильность биологических макромолекул В книге рассмотрены строение и свойства биополимеров — в основном белков. Такие ...
 Влияние тяжелых металлов на процессы биохимического окисления органических веществ
Влияние тяжелых металлов на процессы биохимического окисления органических веществ В научной монографии рассмотрены основные направления очистки сточных вод, ...
 Планета вирусов
Планета вирусов Вирусы — невидимые, но активные участники борьбы за место в биосфере Земли. С их ...
Учебное пособие освещает систематизированную совокупность современных знаний ...