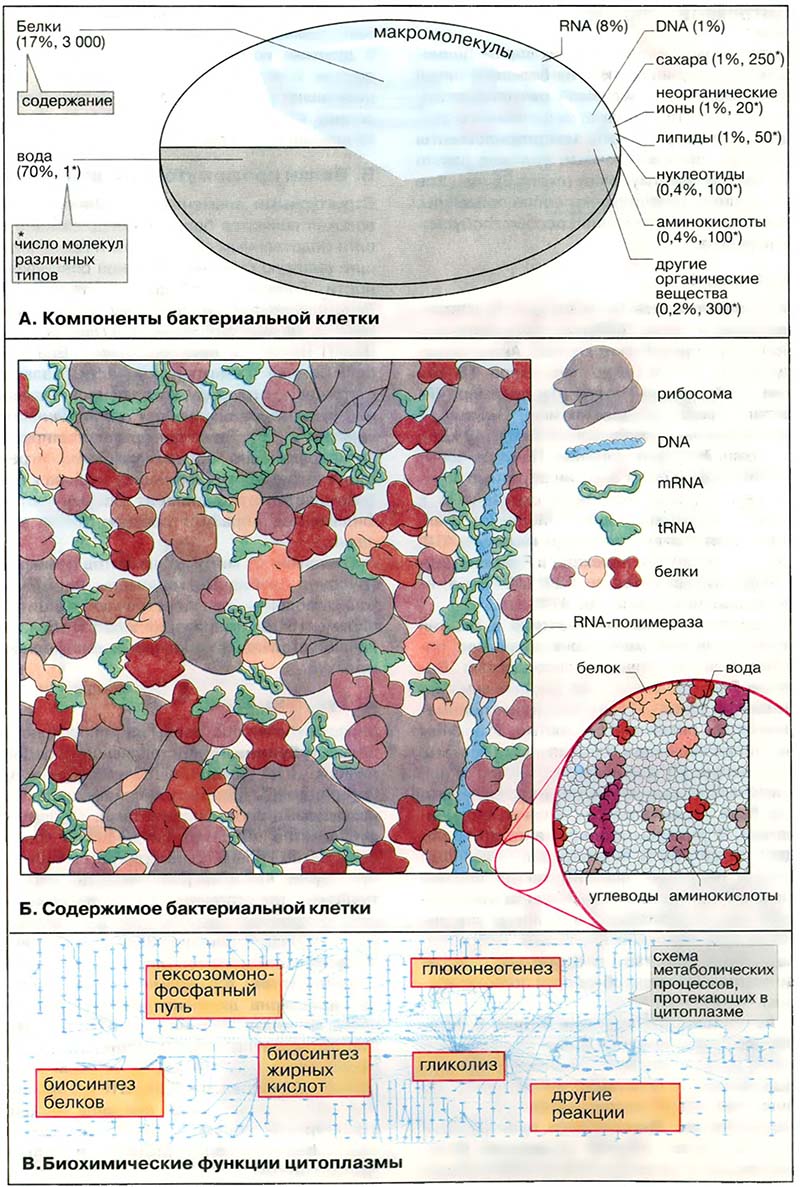
На схеме приведён участок цитоплазмы E. coli (длиной около 100 нм), составляющий 1/600 объёма клетки; увеличение 1×106. При таком увеличении размер атома углерода соответствует крупинке соли, а молекулы АТФ — рисовому зёрнышку. В целях упрощения небольшие по размерам молекулы, такие, как вода, кофакторы и метаболиты, на рисунке не приведены (они показаны в увеличенном виде внизу справа).
В таком участке цитоплазмы содержатся:
— сотни макромолекул, необходимых для синтеза белков, то есть 30 рибосом, более чем 100 белковых факторов, 30 молекул аминоацил-тРНК-синтетаз, 340 молекул тРНК (tRNA), 2-3 мРНК (mRNA) (каждая из которых по размерам 10-кратно превышает приведённый участок клетки) и 6 молекул РНК-полимеразы;
— около 300 молекул других ферментов, включая 130 гликолитических ферментов и 100 ферментов цитратного цикла;
— 30 000 небольших органических молекул с молекулярной массой от 100 до 1 000 Да, например продукты промежуточного метаболизма и коферменты (показаны в 10-кратном увеличении внизу справа);
— наконец, 50 000 неорганических ионов; остальной объем занимает вода.
Схема иллюстрирует тот факт, что цитоплазма клеток заполнена макромолекулами и малыми органическими молекулами, причём макромолекулы расположены очень близко друг к другу: большинство из них разделено лишь несколькими молекулами воды. Все эти молекулы находятся в постоянном движении. Однако повторяющиеся столкновения предотвращают их движение в каком-либо определённом направлении. В действительности они движутся беспорядочно по зигзагообразным траекториям. Белки из-за большой массы движутся особенно медленно. Тем не менее, средняя скорость миграции составляет около 5 нм/мс, то есть за 2 мс они проходят расстояние, равное диаметру белковой глобулы. По статистической оценке любой белок может достичь любой точки в клеточной цитоплазме менее чем за секунду.
В таком участке цитоплазмы содержатся:
— сотни макромолекул, необходимых для синтеза белков, то есть 30 рибосом, более чем 100 белковых факторов, 30 молекул аминоацил-тРНК-синтетаз, 340 молекул тРНК (tRNA), 2-3 мРНК (mRNA) (каждая из которых по размерам 10-кратно превышает приведённый участок клетки) и 6 молекул РНК-полимеразы;
— около 300 молекул других ферментов, включая 130 гликолитических ферментов и 100 ферментов цитратного цикла;
— 30 000 небольших органических молекул с молекулярной массой от 100 до 1 000 Да, например продукты промежуточного метаболизма и коферменты (показаны в 10-кратном увеличении внизу справа);
— наконец, 50 000 неорганических ионов; остальной объем занимает вода.
Схема иллюстрирует тот факт, что цитоплазма клеток заполнена макромолекулами и малыми органическими молекулами, причём макромолекулы расположены очень близко друг к другу: большинство из них разделено лишь несколькими молекулами воды. Все эти молекулы находятся в постоянном движении. Однако повторяющиеся столкновения предотвращают их движение в каком-либо определённом направлении. В действительности они движутся беспорядочно по зигзагообразным траекториям. Белки из-за большой массы движутся особенно медленно. Тем не менее, средняя скорость миграции составляет около 5 нм/мс, то есть за 2 мс они проходят расстояние, равное диаметру белковой глобулы. По статистической оценке любой белок может достичь любой точки в клеточной цитоплазме менее чем за секунду.
Статьи раздела «Клеточные компоненты и цитоплазма»:
- Клеточные компоненты и цитоплазма
- А. Компоненты бактериальной клетки
- Б. Содержимое бактериальной клетки
- В. Биохимические функции цитоплазмы
- Цитоскелет: состав
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 NMR Studies of Structural Motifs: Protein Folding and Ligand Binding
NMR Studies of Structural Motifs: Protein Folding and Ligand Binding NMR of Structural Motifs: The agrin G3 domain is critical in development and maintenance of the neuromuscular junction. G3 binds -dystroglycan and ...
 Asphaltenes: Chemical Transformation during Hydroprocessing of Heavy Oils (Chemical Industries)
Asphaltenes: Chemical Transformation during Hydroprocessing of Heavy Oils (Chemical Industries) During the upgrading of heavy petroleum, asphaltene is the most problematic impurity since it is the main cause of catalyst deactivation and sediments ...
 Handbook of Nanoindentation: With Biological Applications
Handbook of Nanoindentation: With Biological Applications Broadly divided into two parts, this guide’s first part presents the a’basic sciencea’ of nanoindentation, including the background of contact ...
As the title suggests, Isotope Effects in the Chemical, Geological and Bio Sciences deals with differences in the properties of isotopically ...