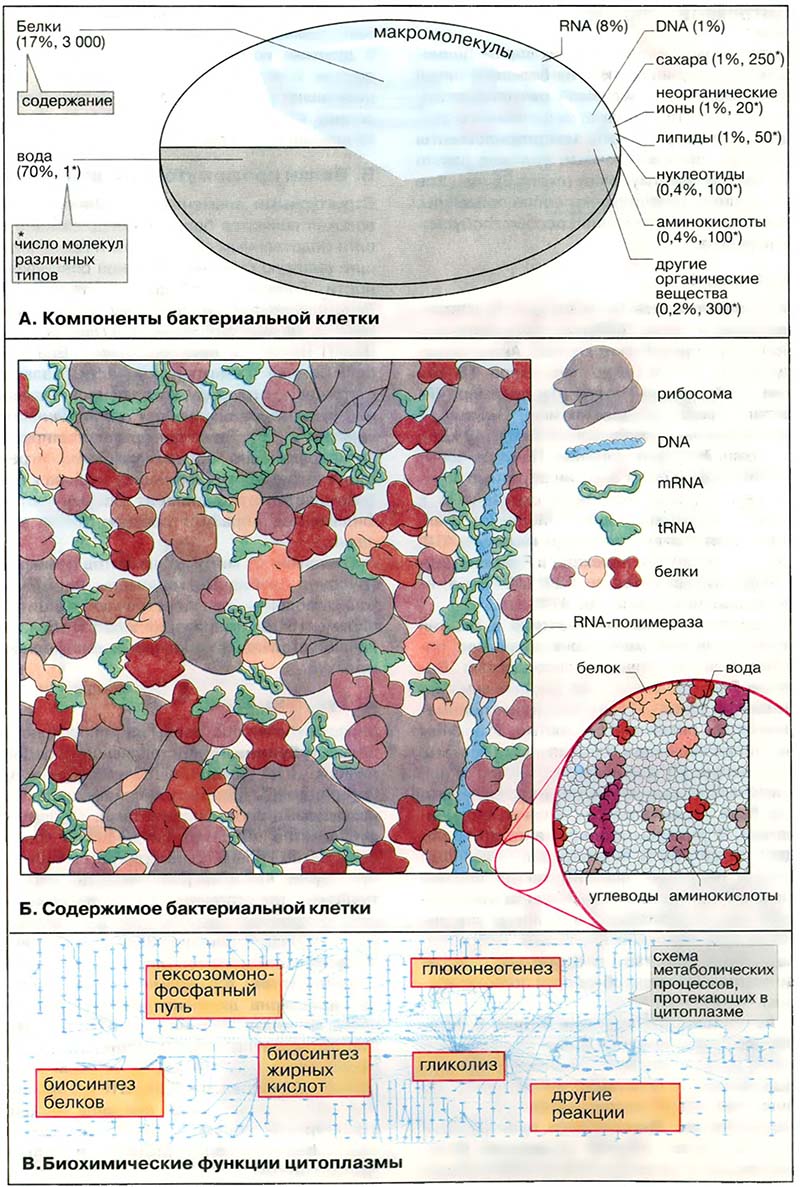
Основным компонентом всех клеток является вода (70 %). Остальная часть — это макромолекулы (белки, нуклеиновые кислоты, полисахариды), небольшие органические молекулы и неорганические ионы. Наиболее распространёнными из макромолекул являются белки, составляющие до 55 % сухого веса клетки.
Единичная клетка E. coli имеет объём около 0,88 мкм3. По одной шестой этого объёма составляют мембраны и ДНК (DNA) («нуклеоид»). Оставшееся внутреннее пространство заполнено цитоплазмой (не «цитозолем», см. Центрифугирование). С учётом ряда допущений относительно размера белков (средняя молекулярная масса 40 кДа) и их распределения в клетке можно считать, что цитоплазма клетки E. coli содержит приблизительно 250 000 белковых молекул. В эукариотических клетках, которые примерно в 1 000 раз больше, число белковых молекул можно оценить в несколько миллиардов.
Единичная клетка E. coli имеет объём около 0,88 мкм3. По одной шестой этого объёма составляют мембраны и ДНК (DNA) («нуклеоид»). Оставшееся внутреннее пространство заполнено цитоплазмой (не «цитозолем», см. Центрифугирование). С учётом ряда допущений относительно размера белков (средняя молекулярная масса 40 кДа) и их распределения в клетке можно считать, что цитоплазма клетки E. coli содержит приблизительно 250 000 белковых молекул. В эукариотических клетках, которые примерно в 1 000 раз больше, число белковых молекул можно оценить в несколько миллиардов.
Статьи раздела «Клеточные компоненты и цитоплазма»:
- Клеточные компоненты и цитоплазма
- А. Компоненты бактериальной клетки
- Б. Содержимое бактериальной клетки
- В. Биохимические функции цитоплазмы
- Цитоскелет: состав
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Molecular Biology of the Cell: The Problems Book
Molecular Biology of the Cell: The Problems Book The Problems Book helps students appreciate the ways in which experiments and simple calculations can lead to an understanding of how cells work by ...
 Молекулярные механизмы взаимодействия эндотоксинов с клетками-мишенями
Молекулярные механизмы взаимодействия эндотоксинов с клетками-мишенями Открытие истинных рецепторов к эндотоксинам (липополисахаридам), сделанное на ...
В книге обобщаются современные достижения сравнительно новой отрасли знания, ...
