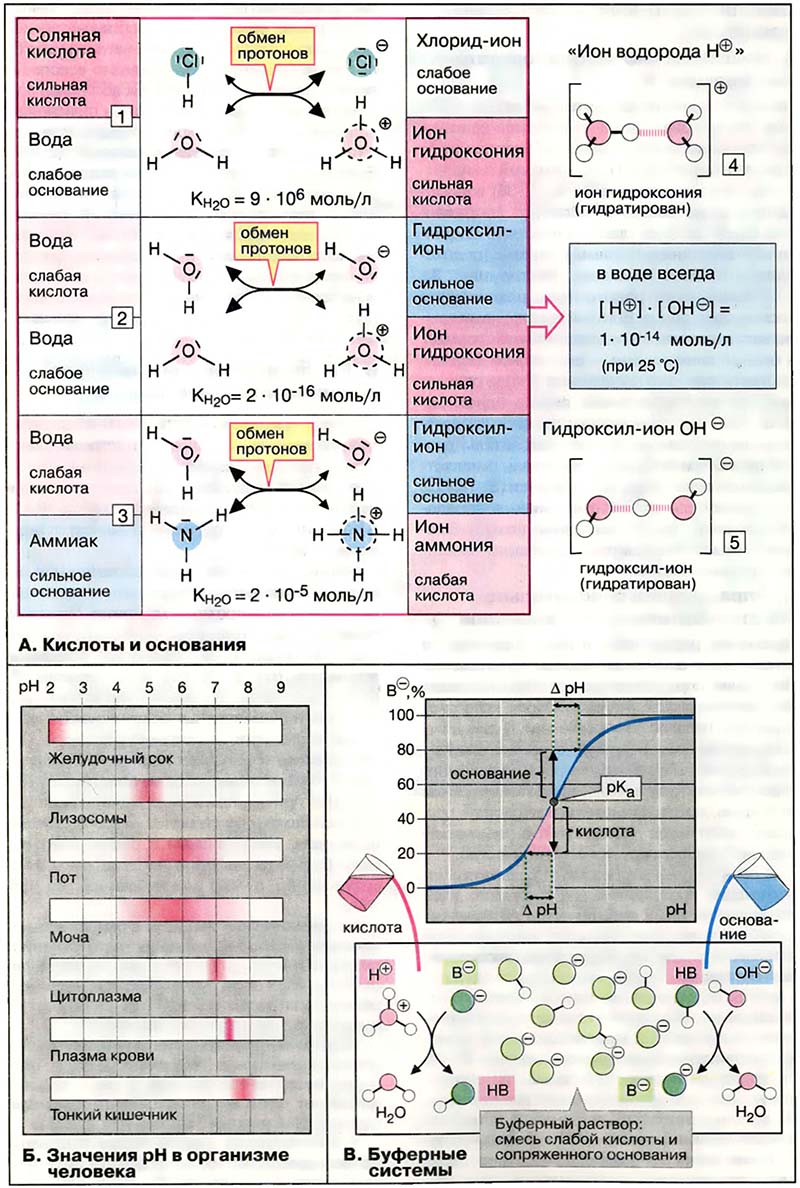
В клетках и межклеточных жидкостях pH поддерживается на относительно постоянном уровне. В крови величина pH обычно меняется в пределах 7,35-7,45 (см. Кислотно-основной баланс). Это соответствует изменению концентрации водородных ионов не более чем на 30 %. В цитоплазме pH составляет 7,0-7,3, что несколько меньше, чем в крови. В лизосомах (см. Лизосомы, pH 4,5-5,5) концентрация водородных ионов более чем в 100 раз выше по сравнению с концентрацией в цитоплазме.
В пищеварительном тракте, который для организма является как бы внешним миром, и в выделениях организма pH варьирует в существенно большей степени. Экстремальные величины pH (около 2) наблюдаются в желудке и в тонком кишечнике (менее 8). В связи с тем, что почки могут выделять как кислоты, так и основания (см. Экскреция протонов и аммиака), значительные вариации pH (4,8-7,5) наблюдаются в моче.
В пищеварительном тракте, который для организма является как бы внешним миром, и в выделениях организма pH варьирует в существенно большей степени. Экстремальные величины pH (около 2) наблюдаются в желудке и в тонком кишечнике (менее 8). В связи с тем, что почки могут выделять как кислоты, так и основания (см. Экскреция протонов и аммиака), значительные вариации pH (4,8-7,5) наблюдаются в моче.
Статьи раздела «Кислоты и основания»:
- А. Кислоты и основания
- Б. Значения pH в организме человека
- В. Буферные системы
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Molecular Biology of the Cell: The Problems Book
Molecular Biology of the Cell: The Problems Book The Problems Book helps students appreciate the ways in which experiments and simple calculations can lead to an understanding of how cells work by ...
 Biological Aging: Methods and Protocols
Biological Aging: Methods and Protocols Biological Aging: Methods and Protocols investigates the various processes that are affected by the age of an organism. Several new tools for the ...
 Биоматериалы, искусственные органы и инжиниринг тканей
Биоматериалы, искусственные органы и инжиниринг тканей Данная книга рассказывает о разработках, проводимых на стыке многих научных ...