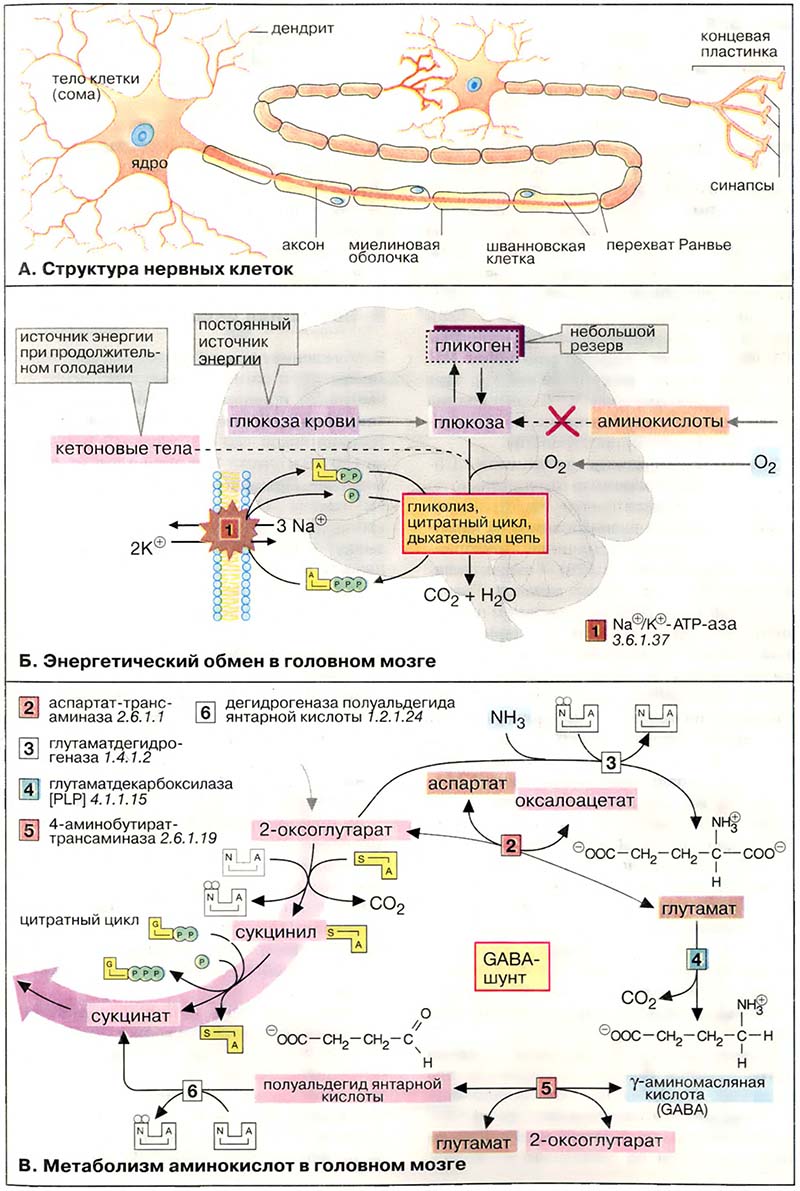
Головной мозг хорошо снабжается кровью и имеет интенсивный энергетический обмен. Хотя головной мозг составляет около 2 % массы тела, при спокойном состоянии организма он утилизирует около 20 % поглощённого кислорода и 60 % глюкозы, которая полностью окисляется до CO2 и H2O в цитратном цикле и путём гликолиза.
В клетках головного мозга практически единственным источником энергии, который должен поступать постоянно, является глюкоза. Только при продолжительном голодании клетки начинают использовать дополнительный источник энергии — кетоновые тела (см. Метаболизм липидов). Запасы гликогена в клетках головного мозга незначительны. Жирные кислоты, которые в плазме крови транспортируются в виде комплекса с альбумином, не достигают клеток головного мозга из-за гематоэнцефалического барьера. Аминокислоты не могут служить источником энергии для синтеза АТФ (АТР), поскольку в нейронах отсутствует глюконеогенез. Зависимость головного мозга от глюкозы означает, что резкое падение уровня глюкозы в крови, например, в случае передозировки инсулина у диабетиков, может стать опасным для жизни.
В клетках центральной нервной системы наиболее энергоёмким процессом, потребляющим до 40 % производимого АТФ, является функционирование транспортной Nа+/K+-АТФ-азы (Na+/K+-«насосa») клеточных мембран [1] (см. Транспортные процессы). Активный транспорт ионов Na+ и K+ компенсирует постоянный поток ионов через ионные каналы. Кроме того, АТФ используется во многих биосинтетических реакциях.
В клетках головного мозга практически единственным источником энергии, который должен поступать постоянно, является глюкоза. Только при продолжительном голодании клетки начинают использовать дополнительный источник энергии — кетоновые тела (см. Метаболизм липидов). Запасы гликогена в клетках головного мозга незначительны. Жирные кислоты, которые в плазме крови транспортируются в виде комплекса с альбумином, не достигают клеток головного мозга из-за гематоэнцефалического барьера. Аминокислоты не могут служить источником энергии для синтеза АТФ (АТР), поскольку в нейронах отсутствует глюконеогенез. Зависимость головного мозга от глюкозы означает, что резкое падение уровня глюкозы в крови, например, в случае передозировки инсулина у диабетиков, может стать опасным для жизни.
В клетках центральной нервной системы наиболее энергоёмким процессом, потребляющим до 40 % производимого АТФ, является функционирование транспортной Nа+/K+-АТФ-азы (Na+/K+-«насосa») клеточных мембран [1] (см. Транспортные процессы). Активный транспорт ионов Na+ и K+ компенсирует постоянный поток ионов через ионные каналы. Кроме того, АТФ используется во многих биосинтетических реакциях.
Статьи раздела «Нервная ткань»:
- А. Структура нервных клеток
- Б. Энергетический обмен головного мозга
- В. Метаболизм аминокислот
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy with MasteringMicrobiology (3rd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy with MasteringMicrobiology (3rd Edition) The Third Edition of Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy is the most cutting-edge microbiology book available, offering unparalleled currency, ...
 Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking (6th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking (6th Edition) Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking, Sixth Edition is a comprehensive learning system that offers print and media resources as well ...
 Фотосинтез: физико-химический подход
Фотосинтез: физико-химический подход Подробно обосновывается предложенная автором (1995) принципиально новая концепция ...