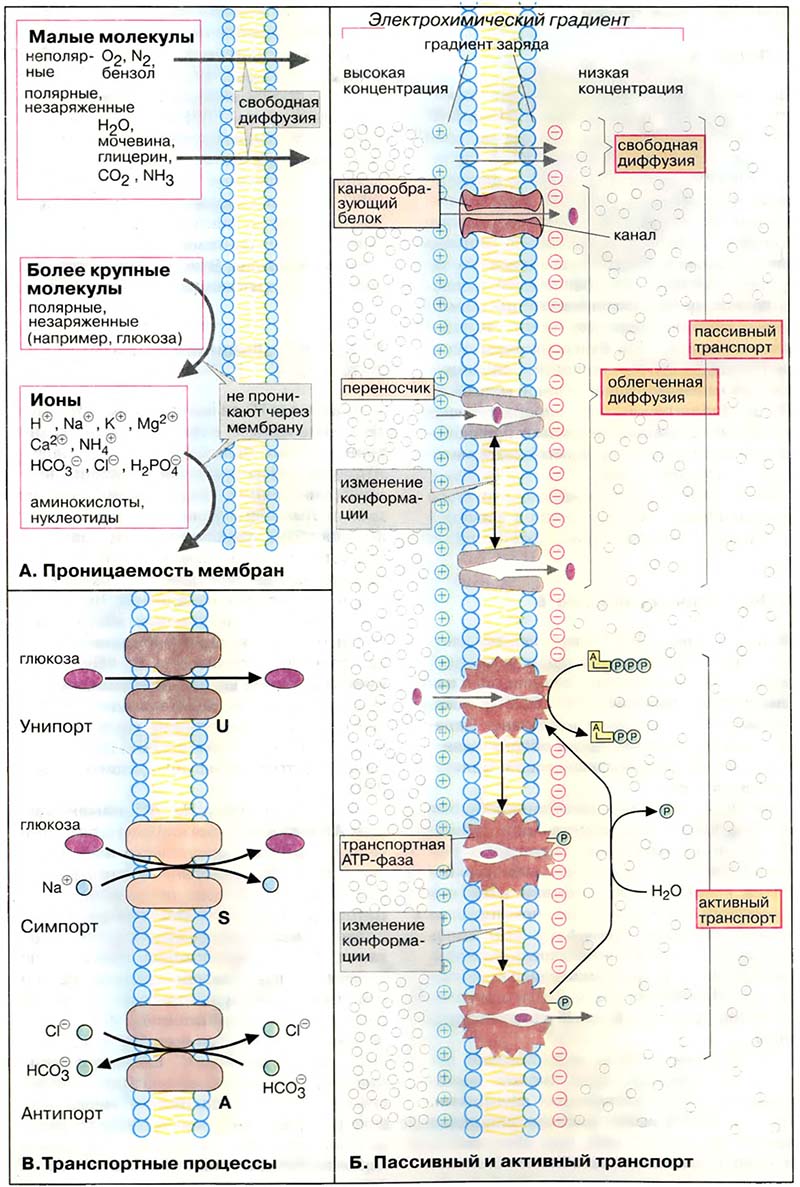
Активный транспорт может идти по механизму унипорта (облегчённой диффузии), согласно которому только одно вещество переносится через биомембрану в одном направлении с помощью канальных или транспортных белков (например, транспорт глюкозы в клетках печени). Активный транспорт может протекать по механизму сопряжённого переноса (симпорт, сопряжённый транспорт), когда два вещества переносятся одновременно в одном направлении как, например, транспорт аминокислот или глюкозы вместе с ионами натрия в кишечных эпителиальных клетках, либо в противоположном направлении (антипорт, обменная диффузия), как, например, обмен ионов HCO3- на Cl- в мембране эритроцитов.
Статьи раздела «Транспортные процессы»:
- А. Проницаемость биомембран
- Б. Пассивный и активный транспорт
- В. Транспортные процессы
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Введение в биофизическую химию
Введение в биофизическую химию Книга представляет собой руководство по биофизической химии, в котором кратко и ...
 Микрокосм. E. coli и новая наука о жизни
Микрокосм. E. coli и новая наука о жизни Цитата «В начале XX в. учёные, стремясь познать природу жизни, начали исследовать ...
 Откровенная наука. Беседы с корифеями биохимии и медицинской химии
Откровенная наука. Беседы с корифеями биохимии и медицинской химии Книга И. Харгиттаи состоит из 36 бесед с выдающимися учёными XX века, работавшими в ...
 Интеллектуальные липидные наноконтейнеры в адресной доставке лекарственных веществ
Интеллектуальные липидные наноконтейнеры в адресной доставке лекарственных веществ Настоящая книга рассказывает о новейших достижениях в использовании липидов и ...