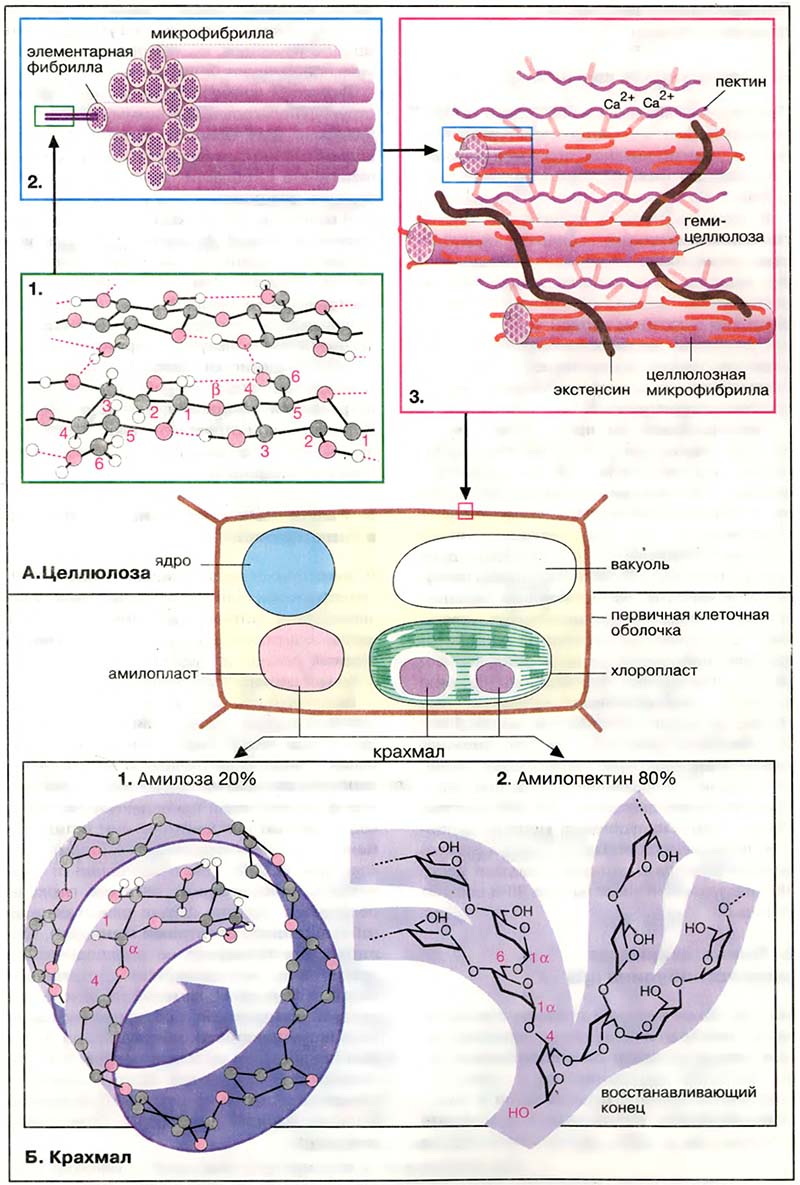
Среди полисахаридов наиболее важными являются два полимера глюкозы растительного происхождения: целлюлоза, в которой остатки глюкозы связаны в положении β(1→4), и крахмал, в котором основной тип связи α(1→4).
Статьи раздела «Растительные полисахариды»:
- Растительные полисахариды
- А. Целлюлоза
- Б. Крахмал
Структура:
Списки:
Сложность материала:
Величины и единицы:
Книги Список книг
 Молекулярные механизмы взаимодействия эндотоксинов с клетками-мишенями
Молекулярные механизмы взаимодействия эндотоксинов с клетками-мишенями Открытие истинных рецепторов к эндотоксинам (липополисахаридам), сделанное на ...
 Лекции по природоведческой микробиологии
Лекции по природоведческой микробиологии Книга основана на курсе лекций, прочитанных в МГУ им. М. В. Ломоносова в 1995-2002 гг. ...
 Нелинейная динамика взаимодействующих популяций
Нелинейная динамика взаимодействующих популяций Проведён анализ режимов динамического поведения в системах нескольких ...